What are the popular capacitor models and product types?
What are the Popular Capacitor Models and Product Types?
I. Introduction
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, playing a crucial role in storing and releasing electrical energy. They are essential for various applications, from filtering signals to stabilizing voltage levels. This article aims to provide an overview of popular capacitor models and product types, helping readers understand their characteristics, applications, and the factors to consider when selecting the right capacitor for a specific use.
II. Basic Concepts of Capacitors
A. What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is a two-terminal passive electronic component that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by an insulating material known as a dielectric. When a voltage is applied across the plates, an electric field is created, allowing the capacitor to store energy. The key parameters of a capacitor include:
1. **Capacitance**: Measured in farads (F), capacitance indicates the amount of charge a capacitor can store per volt of electrical potential.
2. **Voltage Rating**: This is the maximum voltage a capacitor can handle before it risks breakdown or failure.
3. **Tolerance**: This indicates how much the actual capacitance can vary from its stated value.
B. Types of Capacitors Based on Construction
Capacitors can be categorized based on their construction into two main types:
1. **Polarized vs. Non-Polarized**: Polarized capacitors, such as electrolytic capacitors, have a positive and negative terminal and must be connected correctly in a circuit. Non-polarized capacitors, like ceramic capacitors, can be connected in either direction.
2. **Fixed vs. Variable Capacitors**: Fixed capacitors have a set capacitance value, while variable capacitors allow for adjustment of capacitance, making them useful in tuning applications.
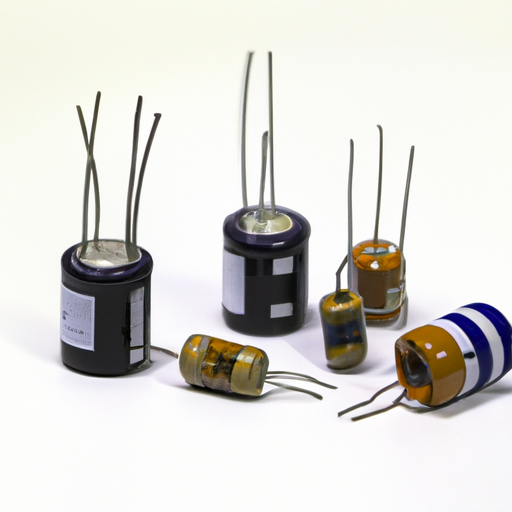
III. Popular Capacitor Models
A. Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are widely used due to their small size, low cost, and reliability. They are made from ceramic materials and are available in various capacitance values.
1. **Characteristics and Applications**: Ceramic capacitors are known for their stability and low losses, making them ideal for high-frequency applications. They are commonly used in decoupling, filtering, and timing circuits.
2. **Common Sub-Types**: Ceramic capacitors are classified into two main categories:
- **Class 1**: These capacitors offer high stability and low losses, suitable for precision applications.
- **Class 2**: These capacitors have higher capacitance values but lower stability, making them suitable for general-purpose applications.
B. Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors are polarized capacitors that use an electrolyte to achieve a larger capacitance value in a smaller package.
1. **Features and Typical Uses**: They are characterized by their high capacitance values and are commonly used in power supply circuits, audio equipment, and energy storage applications.
2. **Advantages and Disadvantages**: While electrolytic capacitors offer high capacitance, they have a limited lifespan and can be sensitive to temperature and voltage fluctuations.
C. Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitors are another type of electrolytic capacitor, known for their stability and reliability.
1. **Unique Properties and Applications**: They have a higher capacitance-to-volume ratio than aluminum electrolytic capacitors, making them suitable for compact electronic devices. They are often used in applications requiring stable capacitance over a wide temperature range.
2. **Comparison with Other Types**: Tantalum capacitors are more expensive than aluminum electrolytics but offer better performance in terms of stability and reliability.
D. Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are made from thin plastic films as the dielectric material.
1. **Types of Film Capacitors**: Common types include polyester, polypropylene, and polystyrene capacitors, each with unique properties and applications.
2. **Applications and Benefits**: Film capacitors are known for their low losses, high insulation resistance, and stability, making them ideal for audio applications, power electronics, and timing circuits.
E. Supercapacitors
Supercapacitors, also known as ultracapacitors, are energy storage devices that bridge the gap between traditional capacitors and batteries.
1. **Definition and Working Principle**: They store energy through electrostatic charge separation, allowing for rapid charge and discharge cycles.
2. **Applications in Energy Storage**: Supercapacitors are used in applications requiring quick bursts of energy, such as in regenerative braking systems, backup power supplies, and energy harvesting devices.
IV. Product Types and Their Applications
A. Surface Mount Capacitors (SMD)
Surface mount capacitors are designed for mounting directly onto the surface of printed circuit boards (PCBs).
1. **Advantages in Modern Electronics**: SMD capacitors are smaller, lighter, and allow for automated assembly, making them ideal for compact electronic devices.
2. **Common Applications**: They are widely used in smartphones, tablets, and other portable electronics.
B. Through-Hole Capacitors
Through-hole capacitors are mounted by inserting their leads into holes on a PCB.
1. **Characteristics and Uses**: They are generally larger than SMD capacitors and provide better mechanical stability, making them suitable for applications where durability is essential.
2. **Comparison with SMD Capacitors**: While SMD capacitors are preferred for compact designs, through-hole capacitors are often used in prototyping and applications requiring higher power handling.
C. Power Capacitors
Power capacitors are designed to handle high voltage and current levels.
1. **Role in Power Electronics**: They are used in power factor correction, energy storage, and voltage regulation applications.
2. **Types and Applications**: Common types include shunt capacitors, series capacitors, and motor run capacitors, each serving specific functions in power systems.
D. Specialty Capacitors
Specialty capacitors are designed for specific applications and environments.
1. **High-Voltage Capacitors**: These capacitors are used in applications requiring high voltage handling, such as power transmission and distribution systems.
2. **RF Capacitors**: Radio frequency capacitors are designed for high-frequency applications, such as in RF amplifiers and oscillators.
3. **Motor Run Capacitors**: These capacitors are used in electric motors to improve efficiency and performance.
V. Factors to Consider When Choosing a Capacitor
When selecting a capacitor for a specific application, several factors should be considered:
A. Capacitance Value and Tolerance
The required capacitance value and its tolerance will determine the capacitor's effectiveness in the circuit.
B. Voltage Rating
Ensure that the voltage rating of the capacitor exceeds the maximum voltage it will encounter in the application to prevent failure.
C. Temperature Coefficient
Different capacitors have varying temperature coefficients, affecting their performance in temperature-sensitive applications.
D. Size and Form Factor
The physical size and form factor of the capacitor should match the design requirements of the circuit.
E. Application-Specific Requirements
Consider any specific requirements related to the application, such as frequency response, stability, and reliability.
VI. Conclusion
Capacitors are vital components in electronic circuits, serving various functions across a wide range of applications. Understanding the different types of capacitors, their characteristics, and their specific uses can help engineers and hobbyists make informed decisions when selecting capacitors for their projects. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of capacitors in modern electronics will only grow, making it essential to explore and understand these components further.
VII. References
For those interested in delving deeper into the world of capacitors, consider exploring the following resources:
1. "Capacitors: Principles and Applications" by John Smith
2. "The Art of Electronics" by Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill
3. Online resources such as educational websites and manufacturer datasheets for specific capacitor models and types.